NHS Health Scotland. [viewed 24 August 2016] Available from: http://www.healthscotland.com/uploads/documents/20387-PractitionerGuide.pdf RCPSYCH, 2014. NAS Resources [online] Royal College of Psychiatrists (how self-esteem affects mental health). [seen 24 August 2016] Readily available from: Courses for All, no date. Strolling football [online] Paths for All. [seen 27 August 2016] SAMH, no date. Get Active [online] Scottish Association for Mental Health.
Institute of Psychiatry, Health center das Clnicas, Professors of Medicine, University of So Paulo So Paulo/SP, Brazil. Email: [email protected]!.?.! Physical activity is an important public health tool utilized in the treatment and prevention of numerous physical diseases, as well as in the treatment of some psychiatric diseases such as depressive and anxiety conditions. Although the variety of reports of the impacts of exercise on psychological health is progressively increasing, these research studies have actually not yet determined the systems associated with the advantages and threats to mental health associated with exercise. This article evaluates the information offered concerning the relationship between exercise and mental health, specifically attending to the association between exercise and mood. State of mind. Sports. Exercise. A atividade fsica, por seus efeitos no tratamento e na preveno.
de vrias patologias, um importante instrumento de sade pblica, sendo til, inclusive, no tratamento de doenas psiquitricas como transtornos depressivos e ansiosos. Todavia, alm dos benefcios, a atividade fsica tambm est associada a prejuzos para a sade psychological, aparecendo ligada a quadros como" exerccio excessivo" e "sndrome de' overtraining'", segundo alguns estudos. Este artigo procura revisar os conhecimentos disponveis sobre as relaes entre atividade fsica e sade mental, principalmente no que se refere ligao existente entre exerccio e humor. Unitermos: Sade mental, humor, esporte, exerccio. Exercise is suggested to the basic population by numerous medical entities consisting of the Centers for Illness Control and Prevention( CDC )and the American College of Sports Medicine( ACSM) since it is considered a crucial tool for the improvement of public health. In addition, physical activity has increasingly been suggested to people with or without disease in order to enhance their quality of life. On the other hand, physical activity can jeopardize psychological health, particularly when carried out in a more extreme way. The understanding of the impacts of exercise on mental health, for that reason, has the possible to influence, in different aspects, the scientific practice of a psychologist or psychiatrist, on one hand, as an auxiliary tool in the avoidance and treatment of psychiatric illness, and as a tool in the promo of a more acceptable lifestyle, or on the other hand, as a cause of issues that require sufficient medical diagnosis and efficient treatment. Research studies that evaluated the association in between exercise and psychological health were browsed. Only human-based studies written in English were picked. Medline database was consulted for articles launched from 1990 up until 2002, interrelating the following crucial words( in keywords field ):" sports "," workout", "state of mind, "and" depression". This search results page in 762 referrals. All short articles that did not have the primary concentrate on this relationship were left out.
Articles with a concentrate on athletic injuries, personality profiles, athletic performance, drugs( medical or not), and handicapped professional athletes were omitted too. This screening Additional resources resulted in 87 referrals. Bibliographic recommendations in the selected posts and books on the theme were also consulted. 2 It has actually been known for several years that regular physical activity brings benefits to individuals with depressive and stress and anxiety symptoms,15-22 a truth validated in current research studies. 23-25 In addition, exercise enhances the quality of life of patients with nonpsychiatric diseases such as peripheral arterial occlusive disease28 and fibromyalgia29 and helps in the relief of such diverse conditions as nicotine abstinence30 and menopause. Studies have revealed that people without psychiatric symptoms who routinely exercise experience much better state of minds than those who do not,31-34 however, it should be kept in mind that an association.
between enhancement of state of mind and medium- or long-term exercise has actually not regularly been shown for typical people. 33-36 On the other hand, there are research studies reporting enhancement of different other aspects such as self-confidence,37 vigor,38 general well-being, and fulfillment with physical look. 35 The effects of routine physical activity on mood have actually generally been studied utilizing aerobic exercise,38,39 but evidence suggests that anaerobic physical activity, such as body building or flexibility training, can likewise reduce depressive.
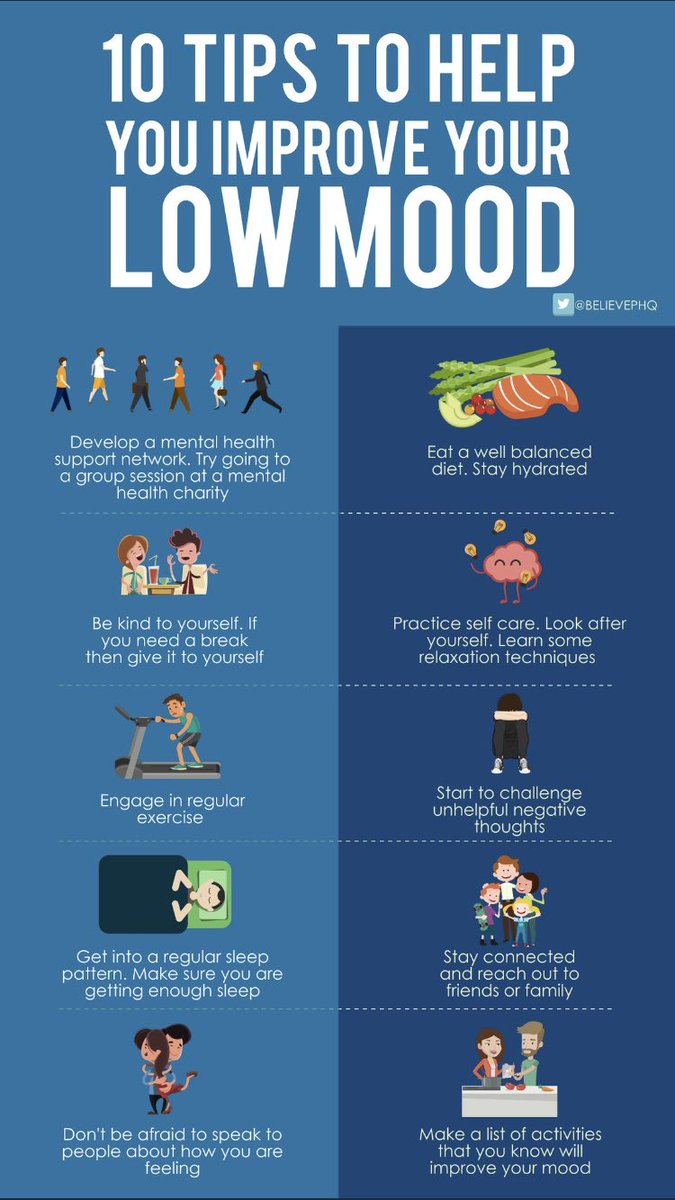
How Your Physical Drug and Alcohol Treatment Center Health Affects Your Mental Health Can Be Fun For Everyone
signs. 18,22,35 In contrast, no agreement exists with regard to anxiety signs, with some authors reporting that anaerobic activity is as efficient as aerobic workout,17 while others do not. 50 Various mental hypotheses have been proposed to explain the advantageous results of physical activity on psychological health, the primary being 1 )diversion, 2) self-efficacy, and 3) social interaction. The interruption hypothesis15 recommends that diversion from undesirable stimuli.
results in an enhanced state of mind throughout and after workout. The http://edwinmyzz539.theburnward.com/how-occupation-affects-mental-health-can-be-fun-for-everyone self-efficacy hypothesis20 proposes that, because workout can be viewed as a difficult activity, the capability to get included in it in a regular way may result in enhanced state of mind and confidence. In addition, physiological hypotheses have actually likewise been raised to describe the impacts of exercise on mental health, the two most studied ones being based on 1 )monoamines and 2 )endorphins. The first hypothesis is supported by the reality that physical activity increases the synaptic transmission of monoamines,15,51 which supposedly work in the very same manner as antidepressive drugs. 15,52 The second hypothesis, nevertheless, is based upon the observation that exercise causes the release of endogenous opioids( endorphins" endogenous morphines"), generally beta-endorphin. 15,51,53 Supposedly, the inhibitory effects of these substances on the central nervous system are accountable for the sensation of calm and improved state of mind experienced after exercise,54 however this has yet to be confirmed. 54 A last unclarified point is the truth that some studies54,56 have reported that opioid receptor blockers such as naloxone or naltrexone decrease the affective action to exercise, thus preferring a role of endorphins, however there are investigations opposing this hypothesis. 35,41,57 No consensus exists concerning the relative importance of the above.
pointed out hypotheses( both mental and physiological) in explaining the association in between exercise and mood enhancement. 35 In order to obtain an accurate definition of this model, a much better understanding of the systems that connect physical activity to each of these hypotheses and of the mechanisms that link these hypotheses to enhanced state of mind is necessary. This knowledge will most likely result in a model in which psychological and biological aspects communicate in a particular and concatenate way, and which varies according to ecological stimuli and the psychological and biological characteristics of each person.