2005; 186( 5 ): 436-441. Corrigan PW., Penn DL. Lessons from social psychology on discrediting psychiatric stigma. American Psychologist. 1999; 54( 9 ):765 -76. Penn DL., Martin J. The preconception of extreme mental illness: Some potential solutions for a recalcitrant problem. Psychiatric Quarterly. 1998; 69( 3 ): 235-47. Hinshaw SP., Cicchetti D. Stigma and mental illness: Conceptions of illness, public mindsets, personal disclosure, and social policy.
2000; 12( 4 ):555 -98. Rosen E., Gregory I. The historical background of irregular psychology. Ed: W.B. Saunders Business. Philadelphia, 1965. Sarason IG., Sarason BR. Abnormal Psychology. The historical background of abnormal psychology, 6th ed. Ed: Prentice Hall. Englewood Cliffs, NJ, 1989. Strickland BR. History and intro to clinical psychology. In S. Cullari Structures of clinical psychology Ed: MA: Allyn & Bacon.
Harty KP. From preconception to technique. Nursing Requirement. 1999; 13( 38 ): 36-40. Furnham A., Chan E. Lay theories of schizophrenia. A cross-cultural contrast of British and Hong Kong Chinese attitudes, attributions and beliefs. Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol. 2004; 39( 7 ):543 -52. Halter MJ. The stigma of looking for care and anxiety. Arch Psychiatr Nurs. 2004; 18( 5 ): 178-84.
The requirement for mental health promo. Aust N Z J Psychiatry. 2001; 35( 6 ):709 -15. Mueller B., Nordt C., Lauber C., Rueesch P., Meyer PC., & Roessler W. Social support customizes viewed stigmatization in the first years of mental disorder: A longitudinal approach. Soc Sci Medication. 2006; 62( 1 ):39? 49. Johnstone MJ. Preconception, social justice and the rights of the mentally ill: Challenging the status quo.
The Main Principles Of How Does Your Environment Affect Your Mental Health
2001; 10( 4 ): 200-209. Lauber C., Carlos N., Wulf R. Lay beliefs about treatments for people with mental health problem and their ramifications for anti preconception strategies. Can J Psychiatry. 2005; 50( 12 ):745 -52. Link BG., Struening EL., Rahav M., Phelan JC., Nuttbrock L. On stigma and its consequences: Evidence from a longitudinal research study of males with dual medical diagnoses of psychological health problem and compound abuse.
1997; 38( 2 ):177 -90. Perlick DA., Rosenheck RA., Clarkin JF., Sirey JA., Salahi J., Struening EL. & Link BG. Preconception as a barrier to recovery: Unfavorable results of viewed preconception on social adjustment of individuals diagnosed with bipolar affective disorder. Psychiatr Serv. 2001; 52( 12 ):1627 -32. Sue D., Sue DW., Sue S. Understanding unusual behavior.
Boston, 1994. Wong DF. Uncovering sociocultural factors influencing the pathway to care of Chinese caretakers with relatives struggling with early psychosis in Hong Kong. Cult Med Psychiatry. 2007; 31( 1 ):51 -71. Hintikka J., Koskela T., Kontula O., Koskela K., Viinamaki H. Men, females and good friends - are there distinctions in relation to mental wellness? Qual Life Res.
Ng CH. The preconception of mental disorder in Asian cultures. Aust N Z J Psychiatry. 1996; 31( 3 ): 382-90. Komiya N., Great GE., Sherrod NB. Psychological openness as a predictor of university student's mindsets towards looking for mental aid. Journal of Counseling Psychology. 2000; 47( 3 ):138 -43. Esters IG., Cooker PG., Ittenbach RF. Impacts of an unit of instruction in psychological health on rural adolescents' conceptions of mental disorder and mindsets about seeking assistance.
Getting The How Does Substance Abuse Affect Your Mental Health To Work
1998; 33( 130 ):469 -76. Weiss MF. Kid's mindsets towards the psychologically ill: An eight-year longitudinal follow-up. Psychol Rep. 1994; 74 (1 ):51 -56. Gaw Air Conditioning. Psychiatric care of Chinese Americans. In A. C. Gaw (Ed.), Culture, Ethnic Take a look at the site here Background, and Mental Health. American Psychiatric Association. Washington DC, 1993. Farina A., Fischer E., Boudreau L., Belt W. Mode of target presentation in determining the stigma of mental illness.
1996; 26 (9 ): 2147-56. Nieradzik K., Cochrane R. Public mindsets towards psychological illness-the results of behaviour, roles, and psychiatric labels. Int J Soc Psychiatry. 1985; 31( 1 ): 23-33. Brown P. Identifying and framing. The Social Construction of Diagnosis and health problem. J Health Soc Behav. 1995; Specification No: 34-52. Schonert - Reichl KA., Muller JR.
Journal of Youth and Teenage years. 1996; 25( 6 ):705 -29. Simmons J. Kid's mental health took on. Counseling Today. 2000; 15( 1 ): 1-26. Leaf PJ., Bruce ML., Tischler GL., Holzer CF. The relationship in between market factors and mindsets towards mental health services. J Community Psychol. 1987; 15( 2 ): 275-84. Corrigan PW - how does menopause affect your mental health., Green A., Lundin R. Kubiak MA., Penn DL.
Psychiatric Providers. 2001; 52( 7 ): 953-58. Stuart H., & Arboleda-Florez J. Neighborhood mindsets towards people with schizophrenia. Can J Psychiatry. 2001; 46( 3 ): 245-52.
Some Alcohol Rehab Facility Known Facts About How Does Menopause Affect Your Mental Health.
Stigma occurs when society identifies somebody as tainted or less desirable. Preconception includes 3 components; an absence of understanding (lack of knowledge), lack of confidences (bias) and people acting in manner ins which drawback the stigmatised person (discrimination) ( 1 ). Numerous health conditions are associated with stigma including some cancers, HIV, AIDS and skin conditions such as psoriasis.
This post discusses psychological health preconception, its effects and what can be done to reduce it. 2 primary types of preconception take place with psychological health issue, social preconception and self-stigma. Social preconception, likewise called public preconception, describes unfavorable stereotypes of those with a mental health problem. These stereotypes concern specify the person, mark them out as different and avoid them being seen as a person.
For example a person with a mental health issue might find that others, consisting of pals and associates, avoid them. They might also find it harder to gain real estate, get work and access healthcare and might find that their account Mental Health Facility is less most likely to be believed by the police if they report a criminal offense. how does lack of sleep affect mental health.
The effects of discrimination, for instance joblessness and social isolation, can stigmatise an individual even more. Self-stigma takes place when a person internalises negative stereotypes. This can trigger low self-esteem, pity and hopelessness. Both types of preconception can lead an individual to prevent looking for aid for their psychological health issue due to humiliation or fear of being shunned or turned down.
An Unbiased View of How Does Mental Health Affect Priests When There Unamable To Marriy
A delay in getting treatment can intensify the outlook of some conditions as can the tension and stress and anxiety caused by experiencing preconception. Member of the family can become stigmatised by a relative having a mental illness, so called courtesy stigma. It has actually been argued that specific diagnostic labels cause stigma. Although it holds true that specific diagnoses, for instance schizophrenia, carry more negative undertones than other diagnoses, for example depression, preconception can not be credited to medical diagnosis alone.
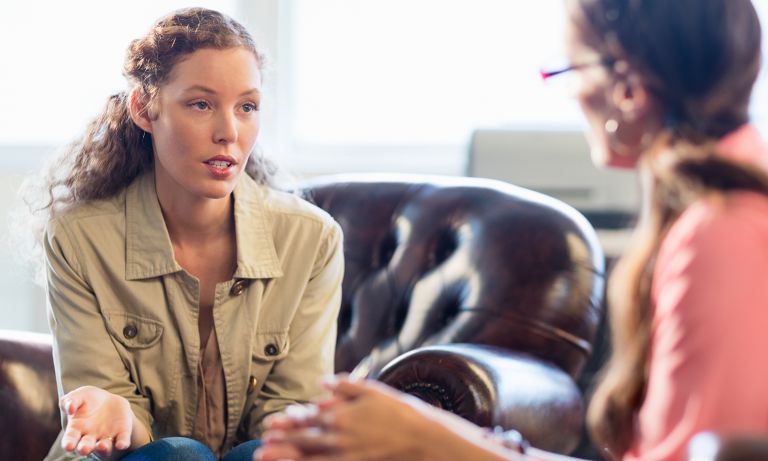

The level of understanding amongst the general public concerning psychological illness is bad and negative beliefs and mindsets are prevalent ( 3 ). Both are crucial elements of preconception. One of the most common and damaging misperceptions is that people with schizophrenia are violent and a threat to others (how bad mental health can affect you newssource). This view has actually been perpetuated by misguiding media reports.
An individual with schizophrenia is far more most likely to be the victim of violence than to be violent to another person ( 5 ). They are also more most likely to be the victim of violence than an individual in the basic population ( 6 ). If an individual with schizophrenia ends up being aggressive this is often related to making use of excessive alcohol or street drugs which is comparable to the scenario seen with individuals who do not suffer from schizophrenia but end up being aggressive.
People with these conditions, and also depression and stress and anxiety, are typically seen as needing to 'pull themselves together'. Such views would rarely be related to cancer or heart problem. In truth the cause of the majority of psychological health issue, like many physical health issues, is complicated and multiple threat factors contribute.